Computer Science and IT
Staffing
Subject Leader – Mr Rawlinson
Curriculum Intent
Computer Science empowers students to understand, shape, and critically evaluate the digital world. At Weavers Academy, we provide a high‑quality computing education that nurtures curiosity, equips learners with robust computational thinking, and develops the technical knowledge and creativity needed to participate confidently and ethically in a rapidly evolving society. Our approach reflects national expectations for computing—combining computer science, information technology, and digital literacy—so that students can apply algorithms, data, and programming to real problems while becoming responsible, capable users of technology.
The Weavers Academy Computer Science team has adapted the curriculum to our context. At its core, our spiraling curriculum is knowledge and skills rich, ensuring students gain the depth of content needed to succeed across computing disciplines. Assessment are summative end‑of‑unit assessments and are complemented by annual assessments.
The Weavers Academy Computer Science Department has high expectations of all members of its community. We are committed to our Academy’s PRIDE values.
Intended Impact
- have their individual needs considered and supported, including those from disadvantaged backgrounds and with SEND, through a curriculum designed with how learners learn in mind;
- benefit from astute sequencing of knowledge‑rich concepts in a spiral progression that leads to deep learning and long‑term retention;
- develop confidence and competence in practical computing: planning solutions, implementing programs, and testing and iterating effectively;
- become proficient in critical thinking and computational problem-solving (abstraction, decomposition, logic, algorithms, data representation);
- engage in healthy debate on digital ethics (e.g., online safety, privacy, cybersecurity, AI and data use), demonstrating responsible digital citizenship;
- develop evaluative skills to analyse data and question anomalies—using spreadsheets and visualisations to draw justified conclusions;
- build resilience and confidence through iterative design and debugging;
- become digitally literate and computing‑literate, understanding the technology they encounter in the news and daily life;
- experience computing‑related cultural capital throughout the curriculum (e.g., diverse role models, real‑world projects, and enrichment);
- understand the breadth of computing and digital careers, making explicit links between content studied and future pathways (software development, data, cybersecurity, UX, networks, digital media, and more).
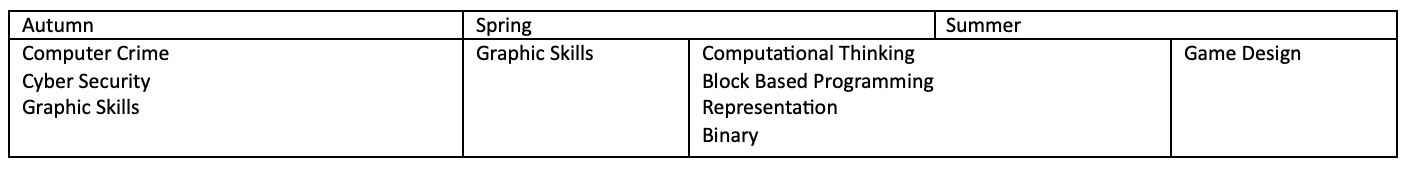
KS3
Our Weavers Academy Computer Science spiral curriculum reviews and builds upon foundational concepts encountered at key stage 2 and the national computing programme of study. Core ideas and topics (algorithms, data, hardware/software, networks, and digital literacy) are revisited each year with increasing complexity.
- Programming (Python): Move from basic sequencing to selection and iteration; design modular solutions using procedures/functions; use appropriate data structures (lists/arrays) and testing strategies to validate programs.
- Data & Spreadsheets: Collect, clean, and analyse data using spreadsheets (formulas, functions, charts), apply graphical techniques to interpret results, and present insights effectively.
- Graphics & Digital Media: Create and evaluate digital artefacts (e.g., raster/vector graphics) with attention to design principles, accessibility, and file formats and compression.
- e‑Safety & Digital Ethics: Demonstrate safe, responsible, and ethical use of technology; understand privacy, online behaviour, cyber risks, and how networks/Internet services function.
- Systems & Representation: Explain how computers represent numbers, text, sound, and images; apply Boolean logic and simple binary operations; understand hardware and software roles.
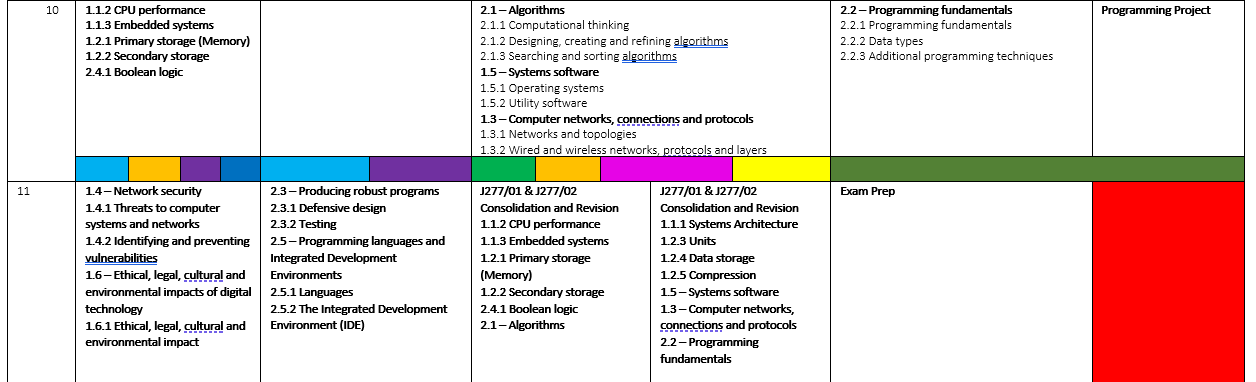
Curriculum Map:
Year 7:

Year 8:
KS4
At key stage 4, students deepen their excitement and curiosity for Computer Science and develop secure understanding of its nature, processes, and methods. We follow OCR GCSE Computer Science (9–1), specification code J277. The qualification has two written papers (1 hour 30 minutes, 80 marks each): Component 1: Computer systems and Component 2: Computational thinking, algorithms and programming. Practical programming skills are assessed within the question papers, with defined sections focusing on programming knowledge and application.
Specification: https://www.ocr.org.uk/Images/558027-specification-gcse-computer-science-j277.pdf
Curriculum Map: